Capacity & Resolution
Visual Working Memory
In addition to having a vast store of long-term memories, the human brain can create short-term memories that last only a few seconds and are essential for performing tasks
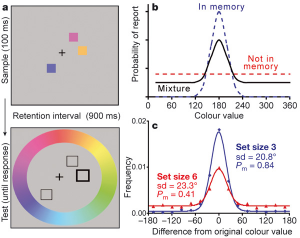
such as adding two numbers or comparing the attractiveness of two faces. Short-term memory can hold only a limited amount of information, but it has not been clear whether we store high-quality representations of a small number of objects (like a small number of high-resolution digital photographs) or low-quality representations of a large number of objects (like a large number of low-resolution digital photographs). Some of our recent research with a color recall paradigm (a) and a mixture model (b) shows that short-term information storage does not discard quality in favor of quantity (c).
Hierarchical Representations
Item & Gist
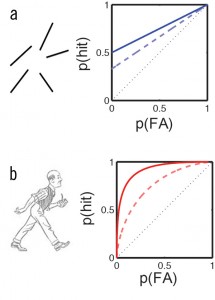
Natural scenes contain discrete item information that can be captured by high threshold model (a) and continuous configural information that can be captured by Signal Detection Theory (b). Thus the Dual-ProcessSignal Detection (DPSD) model has been applied to Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves to separate out the contributions from item and gist information.
Attention
Feature-based Attention
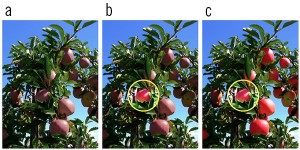
Hypothesized interplay between spatial attention and featural attention in natural vision. A natural scene (a) contains many potentially relevant objects that share common features (the red apples here). Spatial attention can increase the gain in one region of space (b), which may aid in the perception of one of the relevant objects (the apple inside the yellow circle). The simultaneous application of featural attention to objects with relevant features at unattended locations (e.g., the other apples) increases the gain for those objects (c), highlighting them so they may directly influence behavior or become the next target of spatial attention.
Research Methods & Approaches
Psychophysics
Behavioral testing
Cognitive Neuroscience
Use eye tracking, ERP, fMRI, and non-invasive brain stimulation (tDCS & tACS) to understand the underlying neural mechanisms.
Cognitive Modeling
Use Slot mixture model & Dual-process Signal Detection (DPSD) model to separate out dissociable representations in working memory & recognition memory.
Translational Research
Dissociable impairments in memory (e.g., working memory capacity and resolution) in different clinical populations, such as schizophrenia, depression, autism, and MTL patients.
Applied Research
Positive correlation between working memory capacity & fluid intelligence; Negative correlation between working memory resolution & creativity.
